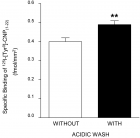
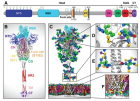
Figure 5
RBD targeted COVID vaccine and full length spike-protein vaccine (mutation and glycosylation role) relationship with procoagulant effect
Luisetto M*, Tarro G, Farhan Ahmad Khan, Khaled Edbey, Mashori GR, Yesvi AR and Latyschev OY
Published: 26 April, 2021 | Volume 5 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-008
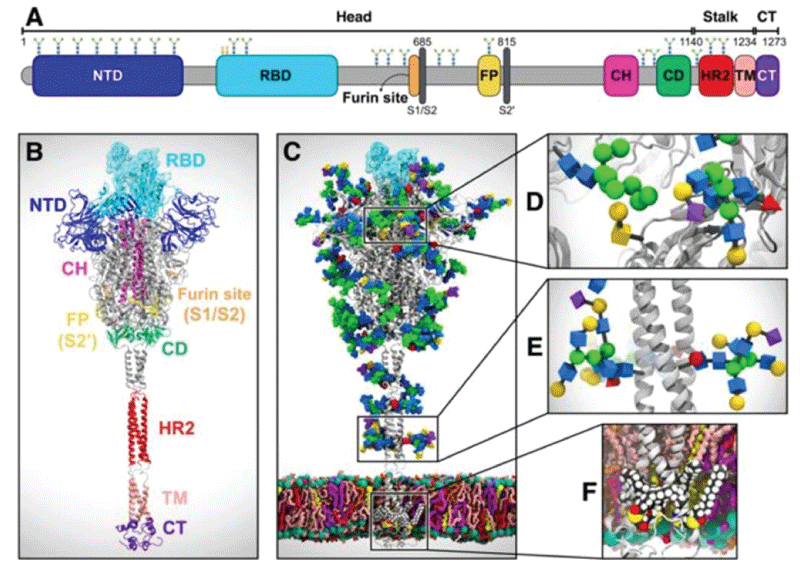
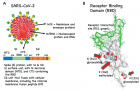
Figure 5:
System overview. (A) A sequence of the full-length spike (S) protein contains the N-terminal domain (NTD, 16-291), receptor binding domain (RBD, 330-530), furin cleavage site (S1/S2), fusion peptide (FP, 788-806), central helix (CH, 987-1034), connecting domain (CD, 1080-1135), heptad repeat 2 (HR2, 1163-1210) domain, transmembrane domain (TD, 1214-1234), and cytoplasmic tail (CT, 1235-1273). Representative icons for N-glycans (blue and green) and O-glycan (yellow) are also depicted according to their position in the sequence. (B) Assembly of the head, stalk, and CT domains into a full-length model of the S protein. (C) Fully glycosylated and palmitoylated model of the Open system. (D-F) Magnified view of the N-/O-glycans rendered using the Symbol Nomenclature for Glycans (SNFG) (D, E) and S-palmitoylation of the cytoplasmic tail (F). from Casalino, et al.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jcavi.1001007 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
More Images
Similar Articles
-
RBD targeted COVID vaccine and full length spike-protein vaccine (mutation and glycosylation role) relationship with procoagulant effectLuisetto M*,Tarro G,Farhan Ahmad Khan,Khaled Edbey,Mashori GR,Yesvi AR,Latyschev OY. RBD targeted COVID vaccine and full length spike-protein vaccine (mutation and glycosylation role) relationship with procoagulant effect. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jcavi.1001007; 5: 001-008
Recently Viewed
-
Febrile Lumbar Pain Revealing a Massive Collection: Complicated Psoas Abscess Managed SurgicallyMohammed Amine Elafari*,Mamad Ayoub,Mohammed Amine Bibat,Rhayour Anas,Maachi Youssef,Amine Slaoui,Tarik Karmouni,Abdelatif Koutani,Khalid Elkhader. Febrile Lumbar Pain Revealing a Massive Collection: Complicated Psoas Abscess Managed Surgically. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001041; 10: 010-012
-
Impact of Microplastics on Human Health through the Consumption of Seafood: A ReviewNeeraj Kumar*,Dev Brat Mishra. Impact of Microplastics on Human Health through the Consumption of Seafood: A Review. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001036; 9: 015-019
-
Phenotypic differences in Obese Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) - A Mini ReviewMichelle Nanni*, Vivian Hu, Swagata Patnaik, Alejandro Folch Sandoval, Johanna Contreras. Phenotypic differences in Obese Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) - A Mini Review. New Insights Obes Gene Beyond. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.niogb.1001020; 8: 001-005
-
Stone on the Mesh: Intravesical Erosion after Laparoscopic Promontofixation-A Hidden Cost of DurabilityAyoub Mamad*,Mohammed Amine Bibat,Mohammed Amine Elafari,Midaoui Moncef,Amine Slaoui,Tarik Karmouni,Abdelatif Koutani,Khalid Elkhader. Stone on the Mesh: Intravesical Erosion after Laparoscopic Promontofixation-A Hidden Cost of Durability. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001040; 10: 006-009
-
Feasibility study on the evaluation of the effect of narrow-band CE-Chirp ASSR in the hearing field after hearing aid in hearing-impaired childrenWang Yonghua*,Xing Shuoyao. Feasibility study on the evaluation of the effect of narrow-band CE-Chirp ASSR in the hearing field after hearing aid in hearing-impaired children. Adv Treat ENT Disord. 2019: doi: 10.29328/journal.ated.1001007; 3: 007-011
Most Viewed
-
Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trialSathit Niramitmahapanya*,Preeyapat Chattieng,Tiersidh Nasomphan,Korbtham Sathirakul. Effects of dietary supplementation on progression to type 2 diabetes in subjects with prediabetes: a single center randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001026; 7: 00-007
-
Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and RehabilitationCristina Popescu, Mircea-Sebastian Șerbănescu, Gigi Calin*, Magdalena Rodica Trăistaru. Physical Performance in the Overweight/Obesity Children Evaluation and Rehabilitation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001030; 8: 004-012
-
Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging PresentationKarthik Baburaj*, Priya Thottiyil Nair, Abeed Hussain, Vimal MV. Hypercalcaemic Crisis Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Rare and Challenging Presentation. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001029; 8: 001-003
-
Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-goDaniel Gandia,Cecilia Suárez*. Exceptional cancer responders: A zone-to-go. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001033; 7: 001-002
-
The benefits of biochemical bone markersSek Aksaranugraha*. The benefits of biochemical bone markers. Int J Bone Marrow Res. 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijbmr.1001013; 3: 027-031

If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."